

Share the latest information



Shanghai, February 22, 2024- Novamab, a biotechnology company dedicated to the research and development of innovative Nonobody drugs, announced today the results of the tolerance, safety, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity characteristics of LQ043H in healthy adult subjects in China after a single administration. The study was registered at the China Clinical Trial Registration Center with China registration number ChiCTR230069500.
This study enrolled a total of 40 healthy subjects. The results showed that compared with the placebo group, LQ043H showed good safety and tolerability after a single inhalation, and there were no treatment-related discontinuations. Pharmacokinetic (PK) studies told that Cmax and AUC increased with dose, and changes of serum LQ043H concentration is consistent with previous expectations. Immunogenicity examination confirmed that no drug related ADA and NAB were observed in all dose groups of subjects avoid of the risk caused by immunogenicity. The results of this study support further research on LQ043H in adult asthma patients in China. Based on the above results, Novamab plans to conduct phase Ib/II clinical studies in asthma patients.
At present, the number of asthma patients who cannot be effectively controlled by basic treatment is gradually increasing in clinical practice, yet there are few large molecule drugs available, and most of them are administered subcutaneously. The inhaled VHH antibody drug LQ043H represents a significant innovation, and the results of the recently completed Phase Ia study are a promising start, with its good safety and tolerability providing strong confidence for the subsequent research..
——Director Hu Wei
The Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University
Principal Investigator of LQ043H Phase Ia
LQ043H is the second product to enter the clinic from Novamab's inhaled biologics development platform, and together with our upcoming Phase II clinical trials in China for LQ036 (an inhaled IL-4Rα VHH antibody drug), it is expected to cover the entire population of patients with moderate to severe asthma. Both LQ043H and LQ036 have the potential to disrupt the existing treatment pathways for respiratory diseases, offering patients a more innovative method of drug administration. They fill a gap in the domestic market for inhaled macromolecules and are the world's first inhaled VHH antibody drugs targeting the same epitope. The clinical team ofNovamab will continue to efficiently advance the phase Ib/II studies of LQ043H. We look forward to the good performance of LQ043H in trials with asthma patient and strive to bring good news to a vast number of asthma patients as soon as possible.
——Wan Yakun
Founder, Chairman, and CEO of Novamab
About asthma
Up to now, asthma remains a globally recognized medical challenge, listed by the World Health Organization as one of the four major persistent diseases, and is the second leading cause of death and disability in the world after cancer. About 350 million people worldwide suffer from asthma, of which about 5% -10% of asthma patients still cannot effectively control their symptoms after treatment with inhaled small molecule drugs [1], indicating a significant unmet clinical need.
According to the GINA guidelines, antibody drugs are suitable for severe patients as an add-on control treatment, serving as a supplementary control medication to the existing medication regimen, which requires long-term use [2]. However, due to the large molecular weight (about 150 kDa) and poor stability of monoclonal antibodies, existing technologies cannot meet the requirements for inhalation administration of large molecules, and can only be treated through intravenous or subcutaneous administration.
Compared with systemic administration through intravenous or subcutaneous administration, inhalation administration has the advantages of good compliance, fast onset, low dosage, minimal systemic exposure, and fewer potential adverse events, making it suitable for a wider range of asthma patients [2]. However, so far, no inhaled macromolecular asthma drugs have been approved for marketing.
About TSLP
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is a short-chain four-alpha-helix bundle type I interleukin-2 (IL-2) family cytokine that can induce monocytes to release chemoattractant factors for T cells, promote the maturation of dendritic cells, and drive the release of downstream T2 cytokines (including IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13, etc.), thereby enhancing the production of IgE, mast cells, and mucus, and increasing airway hyperresponsiveness. TSLP can also activate a variety of cell types involved in non-T2 driven inflammation. TSLP is a key mediator in various phenotypes of asthma, and antibody drugs targeting TSLP and its signal transduction are considered effective strategies for treating asthma.
At present, most of the drugs targeting TSLP under clinical research are monoclonal antibodies, with the drug formulation being subcutaneous injection solutions, and the commercial competition is fierce.
There is an urgent need to introduce differentiated inhaled products.
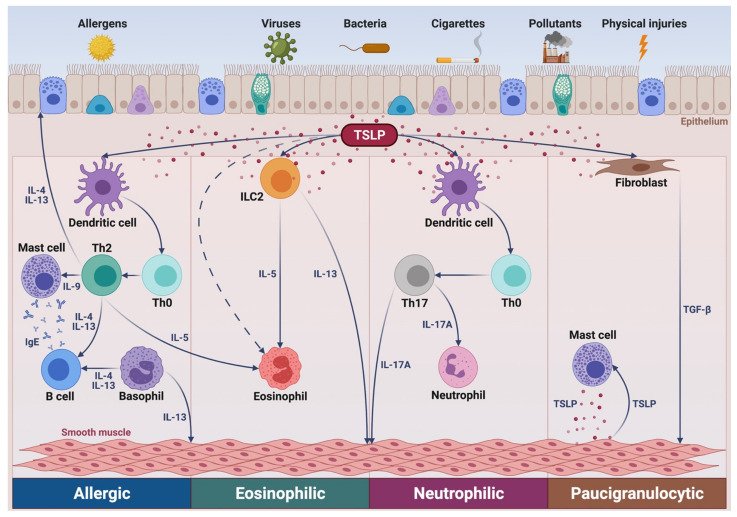
About LQ043H
LQ043H is an anti-TSLP VHH antibody drug with complete independent intellectual property rights developed by Novamab. LQ043H is administered via nebulization inhalation, which allows the drug to directly reach the lung lesion area, acting quickly while avoiding the first-pass effect through the liver and reducing systemic exposure toxicity. It not only leverages the advantages of inhalation administration but also avoids the side effects of subcutaneous injection; LQ043H is compatible with commercially available portable nebulizers, significantly improving patient compliance; LQ043H utilizes a Pichia pastoris production system, with an expression yield as high as 20g/L, which is highly advantageous for commercial promotion; Currently, the sequence, derivatives, and applications of LQ043H have been applied for patent protection in China, Europe, the United States, and other countries/regions, and have been granted a Chinese invention patent (Patent Announcement No. CN114853888B).
References
[1] O'Byrne PM, Panettieri RA Jr, Taube C, Brindicci C, et al. Development of an inhaled anti-TSLP therapy for asthma. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Feb;78:102184.
[2] Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, 2023. Updated May 2023.( Available from: www.ginasthma.org.[3] Pelaia C, Pelaia G, Crimi C, et al. Tezepelumab: A Potential New Biological Therapy for Severe Refractory Asthma. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 22;22(9):4369.



