

Share the latest information



In 2022, among the top 20 best-selling drugs in the world, 8 are macromolecular drugs, and the proportion will be higher if COVID-19 is excluded. The two best-selling drugs Humira and Keytruda are antibody drugs.
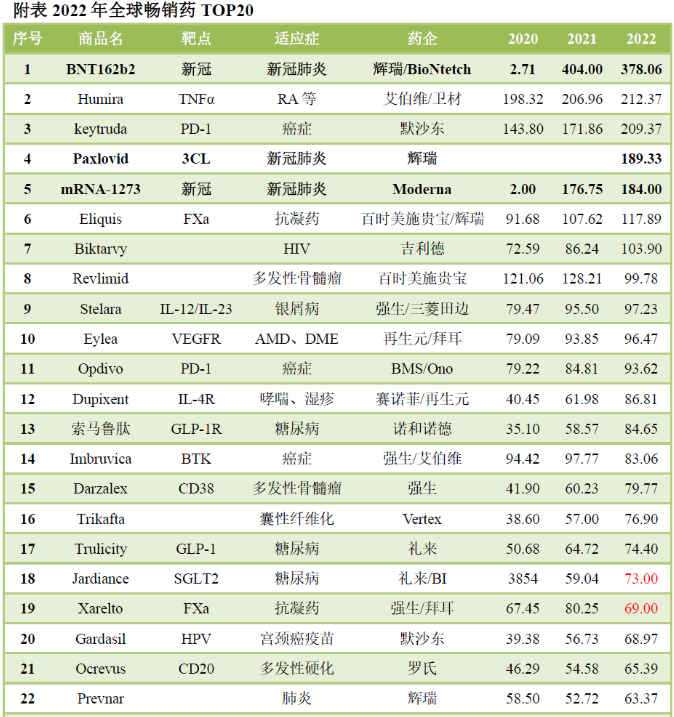
Since its first release in 1986, the FDA has approved a total of 120 antibody drugs, with a market size of $220 billion in 2022.
The 120 antibody drugs that have been launched are all administered by injection, including intravenous injection, subcutaneous injection, vitreous injection, and other methods. For some chronic diseases, the optimization of drug delivery pathways is particularly important, which has become one of the important directions for drug iteration. The treatment of eye diseases with VEGF antibodies or fusion proteins requires complex vitreous injections, so extending the administration cycle has become a competitive focus. From one dose per month to the current four month dose, significant progress has been made. For example, Pfizer acquired Biohaven for $11.6 billion and obtained CGRP small molecule inhibitors. Many companies have developed GLP-1R small molecule inhibitors, PCSK9 oral small molecule or cyclic peptide inhibitors, PD-L1 small molecule inhibitors, etc., hoping to replace injection administration with oral administration.
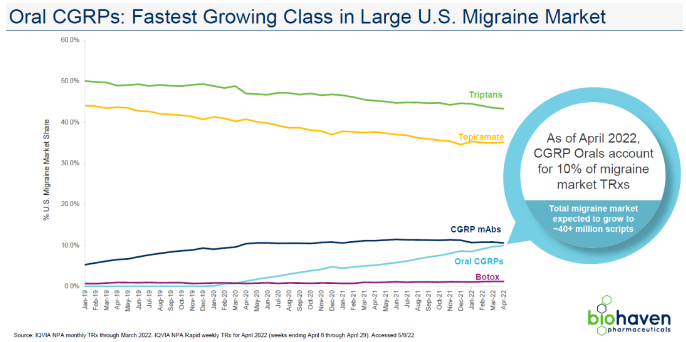
In fact, the innovation of drug delivery pathways for macromolecular drugs has also been actively promoted. Companies such as Novamab Biotechnology, AstraZeneca, and Zaiding Pharmaceuticals have made phased progress in the inhalation or skin administration of antibody drugs.
As a successor to the IL-17 target, Zaiding Pharmaceutical has developed single domain antibodies, which have been proven to achieve transdermal effects through topical administration, and have achieved good preliminary clinical data for mild to moderate psoriasis.
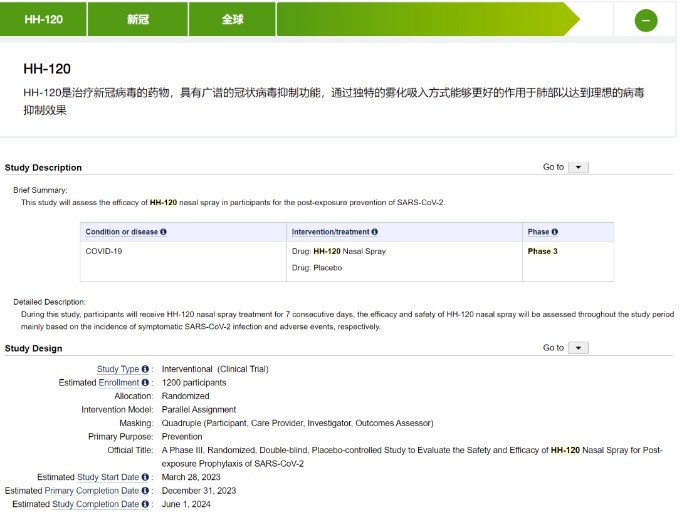
In the COVID-19, some protein vaccines and recombinant protein prophylactic drugs have also achieved nasal spray or aerosol inhalation to prevent infection through mucosal immunity or competitive combination. Huahui Anjian's HH-120 is an ACE2-IgM-Fc fusion protein that is administered through nebulization to achieve post exposure prevention. Currently, it has started Phase III clinical trials.
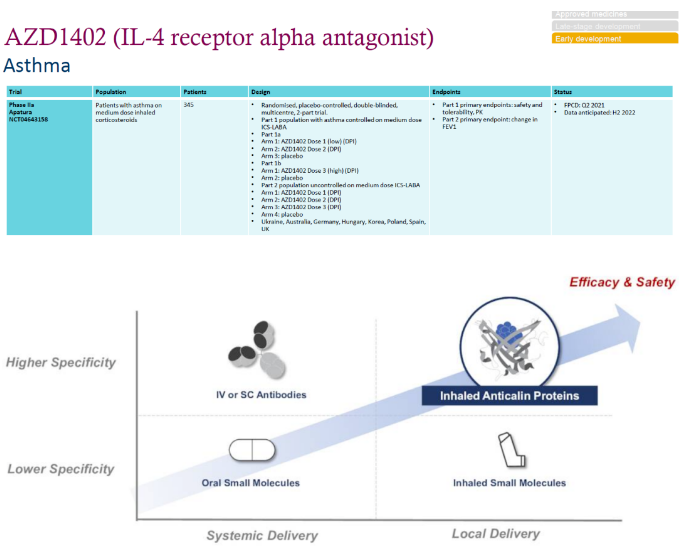
AZD1402, introduced by AstraZeneca from Pieris, is an antibody like molecule that targets the IL-4R pathway and is currently in the second phase of clinical treatment for asthma through inhalation.
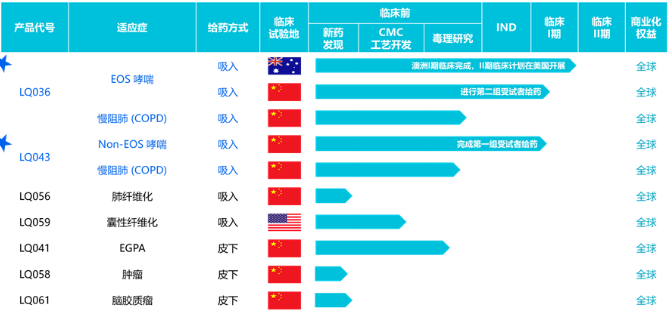
Novamab Biotechnology was established in 2017 and is one of the leading companies in the research and development of inhaled antibody drugs for respiratory diseases. Its IL-4R nanoantibody LQ036 and TSLP nanoantibody LQ043 are both administered by inhalation and are currently in the first phase of clinical research.
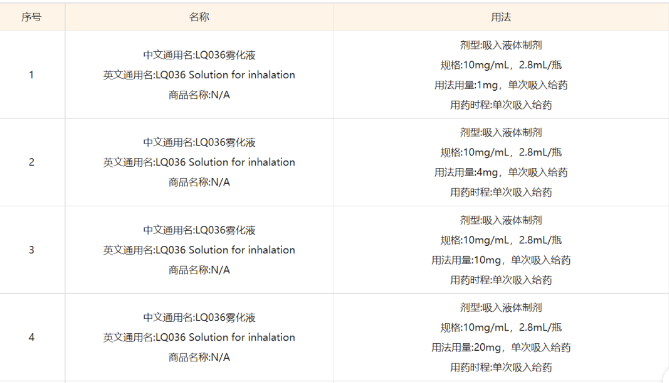
For respiratory diseases, inhalation administration perfectly combines the advantages of nanoantibodies. Taking IL-4R nanoantibody LQ036 as an example, it is mainly used for the treatment of moderate to severe asthma. Inhalation and administration can directly reach the pathological site, with faster onset (2 days of onset, antibody generally takes 4 weeks of onset), and low dosage, only 3% of Dupixent (Dupixent 300mg, LQ036 10mg). Due to the low proportion of drugs entering the blood system (1%), the systemic side effects are very low. In addition, as a nano antibody, LQ036 can be produced using Pichia pastoris, with a production cost much lower than that of animal cell expression, and the production process is easier to scale up, making it very suitable for the needs of long-term medication cycles and large amounts of chronic diseases.
LQ043 is the world's first broad-spectrum asthma/COPD inhaled TSLP nanoantibody therapy drug. Like LQ036, inhalation administration has a faster effect and can reduce dosage, increasing safety. LQ043 is produced using a Pichia pastoris system with a yield of up to 20g/L, and the production cost is much lower than that of antibody drugs expressed in animal cells. It is expected to have the price advantage of small molecule drugs and achieve the efficacy and safety of antibody drugs.
In the R&D pipeline of Novamab Biology, LQ056 for treating pulmonary fibrosis and LQ059 for treating cystic fibrosis are also administered by inhalation.
Summary
In recent years, there has been a lot of progress in the innovation of antibody drug delivery pathways, especially in the original exploration work done by Chinese pharmaceutical companies. Skin diseases, respiratory system diseases, and other diseases are more suitable for developing new macromolecular drug delivery pathways, while single domain antibodies or nanoantibodies are very suitable for such scenarios due to their small molecular weight and strong stability. Luoqi Biotechnology has extensively laid out the treatment of respiratory diseases through inhalation of nano antibodies, and is expected to seize the systematic opportunity of iterative development of heavyweight antibody drugs for respiratory diseases. I believe that the innovation of antibody drug delivery pathways in this category will become milestones in the differential design of iterative drugs, and I look forward to the subsequent clinical progress of these products.



